Everything You Need to Know About Pneumonia: How It Spreads, Treatment Options, and Recovery Signs
Introduction to Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that causes inflammation in the air sacs of the lungs, often leading to fluid or pus accumulation. This condition can result in mild to severe symptoms, affecting people of all ages, but is particularly dangerous for infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Prompt treatment is essential to avoid complications.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options for pneumonia, as well as answer common questions such as “Is pneumonia contagious?” and “Is pneumonia deadly?” Let’s dive in to better understand this disease and how to manage it effectively.
For more information on health blogs visit https://phcworld.com/.
Causes of Pneumonia
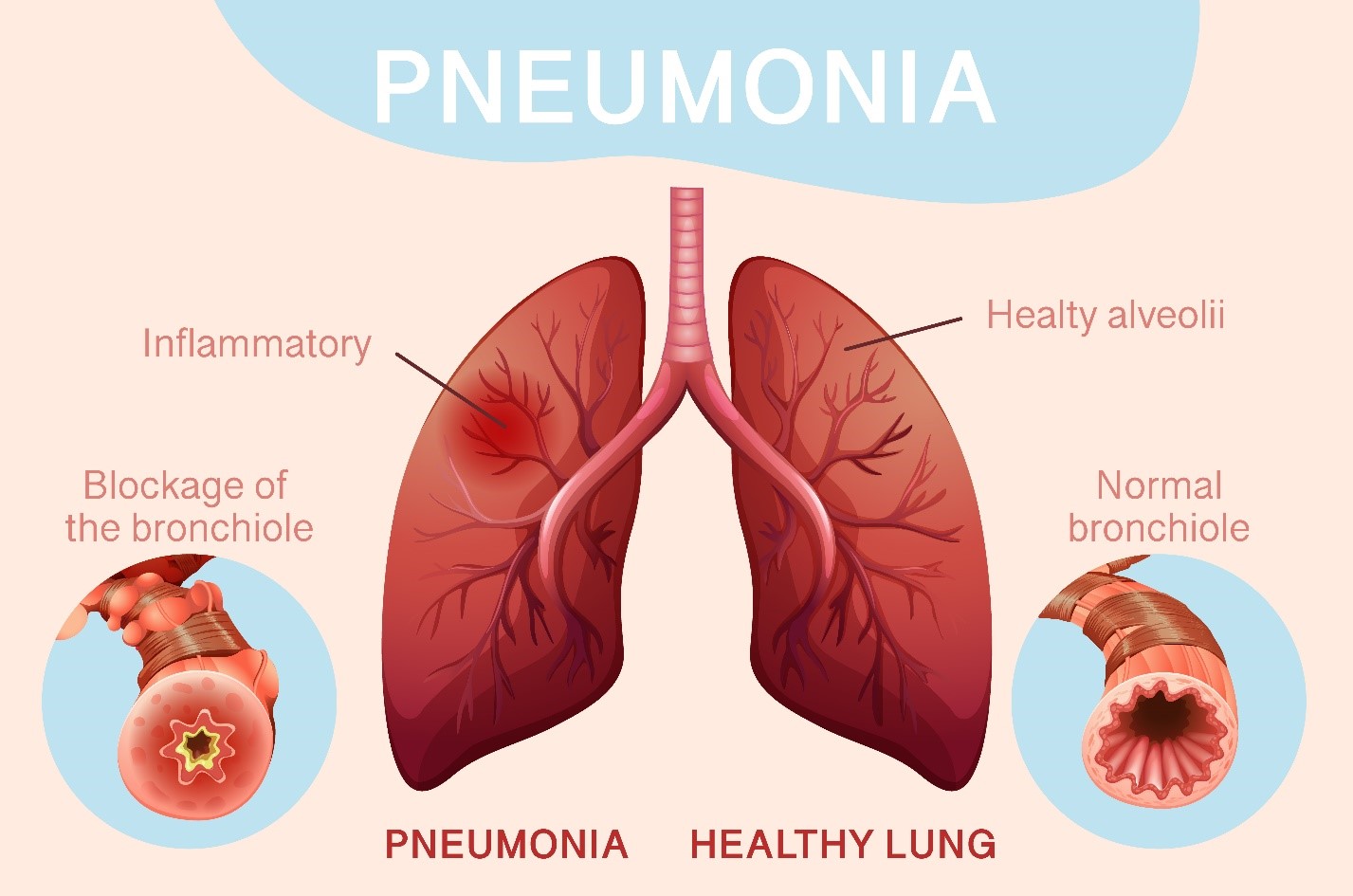
Pneumonia can be caused by various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The most common cause of bacterial pneumonia is *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, which primarily affects adults but can also occur in children. Viral pneumonia, such as that caused by the influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), is often milder but can still lead to severe complications.
Other common causes of pneumonia include:
– **Bacteria**: In addition to *Streptococcus pneumonia*, other bacteria like *Haemophilus influenzae* and *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* can lead to pneumonia.
– **Viruses**: The flu, common cold viruses, and COVID-19 can cause viral pneumonia.
– **Fungi**: Certain fungi found in soil or bird droppings, such as *Histoplasma* or *Coccidioides*, can also result in pneumonia, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
People with chronic illnesses, smokers, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Yes, pneumonia can be contagious depending on its cause. Bacterial and viral pneumonia can spread through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Close contact with an infected individual or touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face can lead to the spread of the infection.
While bacterial pneumonia is less contagious than viral forms, both can be passed from person to person. On the other hand, pneumonia caused by fungi is typically not contagious and results from inhaling fungal spores from the environment.
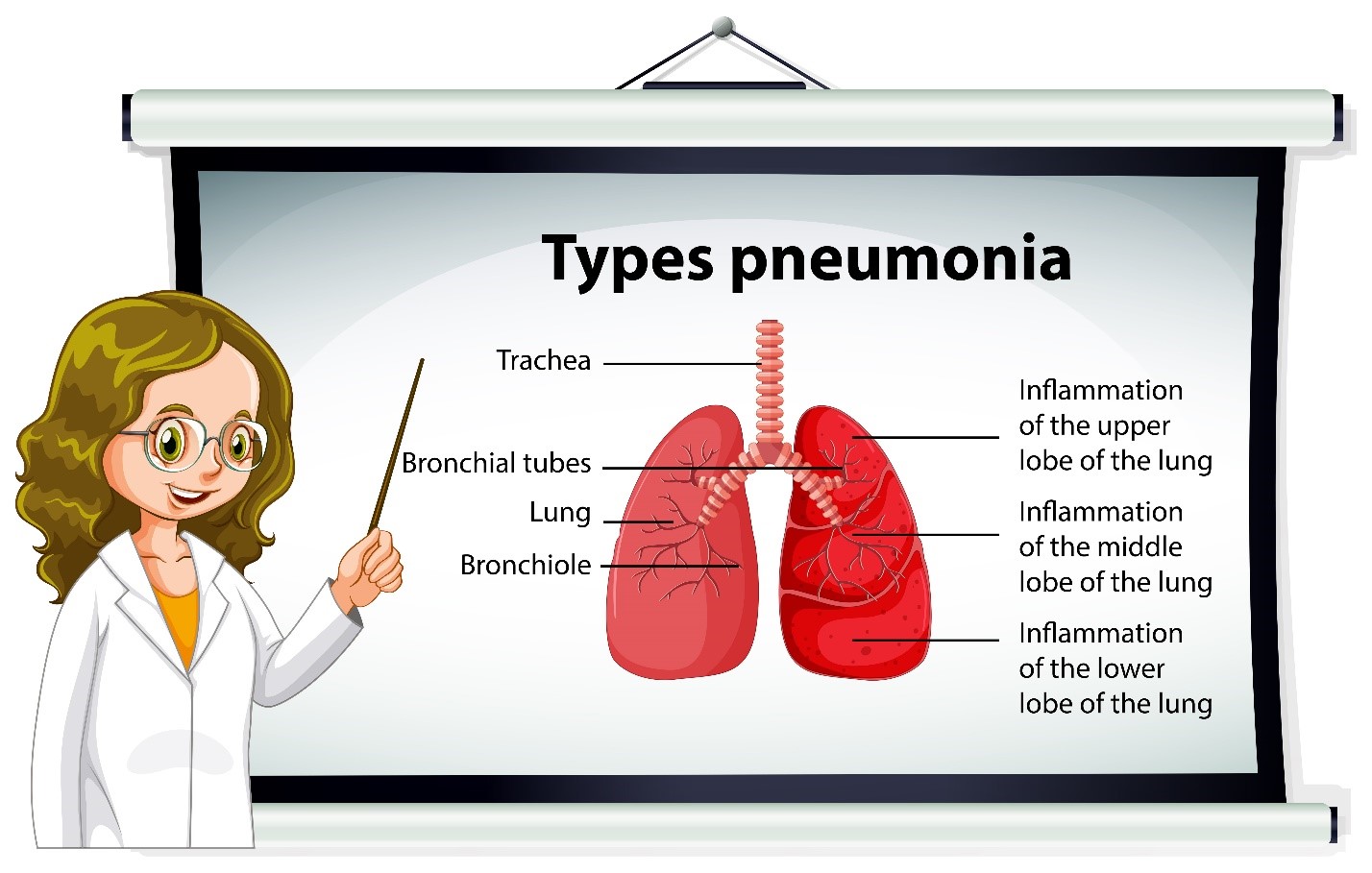
Types of Pneumonia
Pneumonia comes in various forms, and understanding the type helps in managing and treating the condition effectively. The most common types include:
– **Bacterial Pneumonia**: Often caused by *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, this type typically results in sudden symptoms like fever, chills, and shortness of breath. Antibiotics are the primary treatment.
– **Viral Pneumonia**: Caused by influenza, COVID-19, or RSV, this type usually presents with symptoms similar to the flu, such as fever, dry cough, and body aches.
– **Walking Pneumonia**: A milder form of pneumonia caused by *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*, this type doesn’t usually require hospitalization but still requires treatment. Symptoms are less severe but can linger for longer periods.
– **Aspiration Pneumonia**: This occurs when food, liquids, or vomit are inhaled into the lungs, usually due to swallowing difficulties. It often affects individuals with neurological disorders or alcohol use disorders.
– **Fungal Pneumonia**: This type is rare and is caused by fungi like *Histoplasma* or *Coccidioides*. It primarily affects people with weakened immune systems.
Each type of pneumonia has its own treatment approach, which is why identifying the type is crucial for effective management.
Symptoms of Pneumonia in Adults
The symptoms of pneumonia can range from mild to severe, depending on the cause and the person’s overall health. Some common pneumonia symptoms in adults include:
– Fever and chills
– Cough, which may produce phlegm
– Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
– Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
– Fatigue and weakness
– Loss of appetite
– Nausea and vomiting
– Confusion, especially in older adults
If left untreated, pneumonia can worsen and lead to life-threatening complications, such as sepsis, respiratory failure, or lung abscesses. Therefore, it’s important to recognize the signs of pneumonia early and seek medical attention.
Walking Pneumonia vs. Typical Pneumonia
Walking pneumonia is a less severe form of pneumonia, often caused by *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*. Unlike typical pneumonia, which can result in high fever and severe cough, walking pneumonia is characterized by milder symptoms like a dry cough, sore throat, and low-grade fever. People with walking pneumonia can often continue their daily activities without realizing they have pneumonia, hence the name “walking” pneumonia.
However, even though the symptoms are milder, walking pneumonia should still be treated to prevent it from worsening or spreading to others.
Pneumonia Treatment and Medication
Treatment for pneumonia varies based on the type and severity of the infection. The main treatments include:
– **Antibiotics**: These are prescribed for bacterial pneumonia, such as pneumonia caused by *Streptococcus pneumonia*. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve to ensure the infection is fully treated.
– **Antiviral Medications**: If viral pneumonia is the cause, especially from the flu or COVID-19, antiviral drugs may be prescribed.
– **Antifungal Medications**: In cases of fungal pneumonia, antifungal treatments are used to target the specific fungi responsible.
– **Over-the-counter Medications**: Pain relievers, fever reducers, and cough medicines can help manage symptoms, but they do not treat the underlying infection.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for oxygen therapy, intravenous antibiotics, or fluids. Rest, hydration, and proper medical care are crucial for recovery.
Is Pneumonia Curable?
Yes, pneumonia is curable in most cases, especially with prompt and appropriate treatment. Bacterial and viral pneumonia are often treated successfully with antibiotics and supportive care, while mild cases of walking pneumonia can resolve on their own with rest and home remedies.
However, recovery time varies depending on the type of pneumonia and the individual’s health. People with chronic illnesses or compromised immune systems may take longer to recover, and the risk of complications is higher.
In some cases, particularly with severe pneumonia or in individuals with weakened immunity, pneumonia can lead to serious complications. This is why early diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Signs That Pneumonia Is Improving
If you’ve been diagnosed with pneumonia and are undergoing treatment, there are several signs that indicate improvement:
– **Decreasing Fever**: A lower or normalized temperature is often one of the first signs that the body is fighting off the infection.
– **Improvement in Breathing**: Less difficulty breathing or a decrease in shortness of breath is a positive sign.
– **Reduced Coughing**: As the infection subsides, the cough will gradually become less frequent and severe.
– **Increased Energy Levels**: Feeling more energetic and less fatigued is another indication that the body is recovering from pneumonia.
– **Clearer Chest X-rays**: Follow-up x-rays may show reduced lung inflammation, signaling that the infection is clearing up.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation and potential adjustments in treatment.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a potentially serious infection, but with early detection, proper treatment, and care, most people can recover fully. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pneumonia can help in managing the condition effectively. Whether it’s a mild case of walking pneumonia or a more severe bacterial infection, getting the right medical attention is crucial.
Recognizing the signs of pneumonia and knowing when symptoms are improving can help ease concerns during the recovery process. If you suspect you have pneumonia, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider to receive timely and appropriate care.


